Intelligent vehicle highway systems (IVHS) refers to transportation systems that involve integrated applications of advanced surveillance, communications, computer, display, and control process technologies, both in the vehicle and on the highway (Ref. 5).
In 1991, Congress passed the Intermodal Surface Transportation Efficiency Act (ISTEA), which included an authorization of $660 million to create an IVHS program for the nation. The goals for IVHS were defined as follows: to improve safety, to reduce congestion, to enhance mobility, to minimize environmental impact, to save energy, and to promote economic productivity. Research studies and demonstration projects to accomplish these goals are in progress. Funding has continued under subsequent legislation and experimental “smart highways” are being constructed.
The IVHS program is not limited to urban areas. It should result in benefits for both urban and rural drivers, and for both younger and older drivers. People who use public transportation will also benefit, and others will be persuaded to join them.
A planning process was undertaken following the adoption of the act, which identified 28 user services in six categories (Ref. 5):
Travel and traffic management
• Pretrip travel information
• En route driver information
• Traveler services information
• Route guidance
• Ride matching and reservation
• Incident management
• Travel demand management
• Traffic control
Public transportation management
• En route transit information
• Public transportation management
• Personalized public transit
• Public safety security
Electronic payment
• Electronic payment services
Commercial vehicle operations
• Commercial vehicle electronic clearance
• Automated roadside safety inspection
• Commercial vehicle administrative processes
• Onboard safety monitoring
• Commercial fleet management
• Hazardous material incident notification
Emergency management
• Emergency vehicle management
• Emergency notification and personal security
Advanced vehicle safety systems
• Longitudinal collision avoidance
• Lateral collision avoidance
• Intersection collision avoidance
• Vision enhancement for crash avoidance
• Safety readiness
• Precrash restraint deployment
• Automated vehicle operation
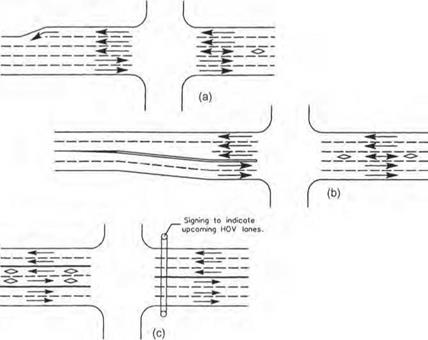
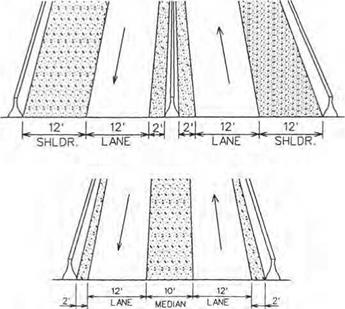
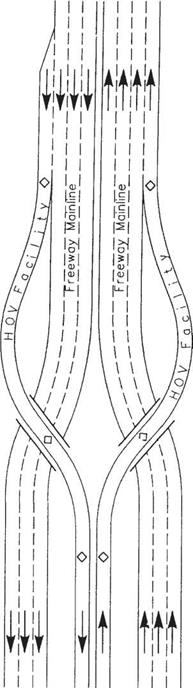
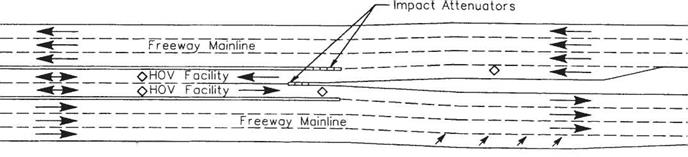
For those services listed under travel and traffic management, the emphasis will be upon providing real-time data to help the driver make the best decisions during a trip or even make last-minute changes in itinerary prior to departure. This category also encourages the use of high-occupancy vehicles and provides traffic control procedures and mechanisms to deal with situations as they occur.
The services under public transportation management will improve the efficiency, safety, and effectiveness of public transportation systems for users and providers alike. Again, the emphasis is on gathering and relaying real-time information to the users of the systems. It provides for automation of operations, planning, and management functions of public systems. It will also be able to monitor the environment in public station areas, including bus stops and parking lots, to generate alarms when necessary and increase public safety.
Electronic payment services will promote intermodal travel by providing a common electronic payment medium for all transportation modes and functions, including tolls, transit fares, and parking. One “smart card” could be used for several different modes of transportation.
Under commercial vehicle operations, trucks and buses equipped with transponders could have their safety status, credentials, and weight checked at mainline speeds. Vehicles passing the check would not have to pull over into the inspection/weigh facility. Automated safety inspections would allow “real-time” access at the roadside to the performance record of carriers, vehicles, and drivers. By using sensors and diagnostic equipment, vehicle systems and even driver alertness can be checked without stopping the vehicle.
Under emergency management, the capabilities of fleet management, route guidance, and signal priority can be used for emergency vehicles. Police, fire, and medical units can be directed over the most expeditious route to an incident site using real-time information. Driver and personal security systems will allow the user to initiate distress signals for incidents like mechanical breakdowns. Automatic collision notification would send information regarding location, nature, and severity of the incident to emergency personnel.
Concerning those services under advanced vehicle safety systems, a series of collision avoidance systems would be developed. For potential longitudinal, lateral, and intersection collisions, the systems would be able to sense impending trouble, warn the driver, and temporarily control the vehicle. On attempted lane changes, the driver’s blind spot would be monitored, and the vehicle prevented from making the switch if a vehicle was present. Another possibility is vision enhancement for the driver, in which the roadway and roadside are continuously scanned for potential hazards and the driver is made aware of situations when necessary. In-vehicle equipment can be used to monitor the driver’s condition and issue appropriate warnings. In employing precrash restraint deployment, the velocity, mass, and direction of the vehicles and objects involved in a potential crash are identified and the number, location, and physical characteristics of occupants are determined. This information in turn is used to trigger responses, such as tightening of lap-shoulder belts, arming and deploying air bags at optimal pressure, and deploying roll bars. Another program being investigated is automated vehicle operation. This would ultimately provide an accident-free environment on the roadway. Drivers would be able to buy a vehicle already equipped to drive under these conditions, or purchase instrumentation and have it installed on an existing vehicle.







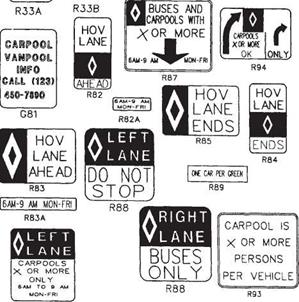
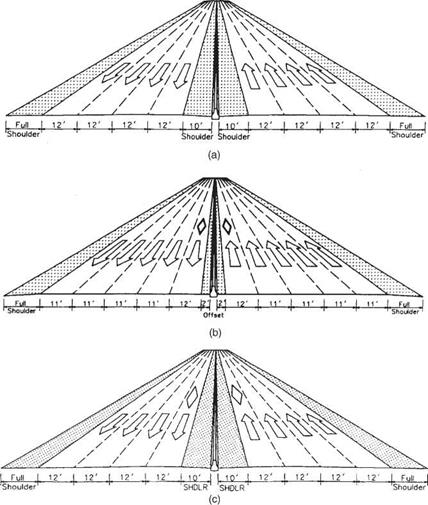
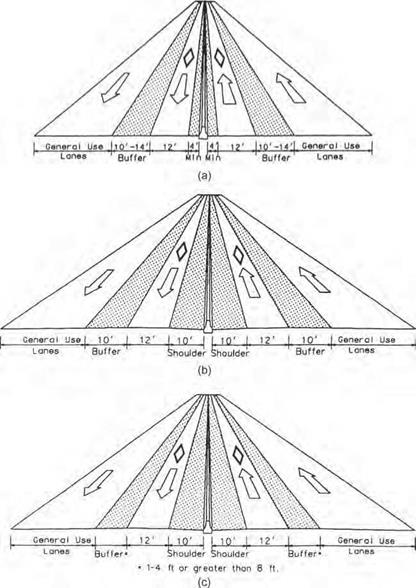
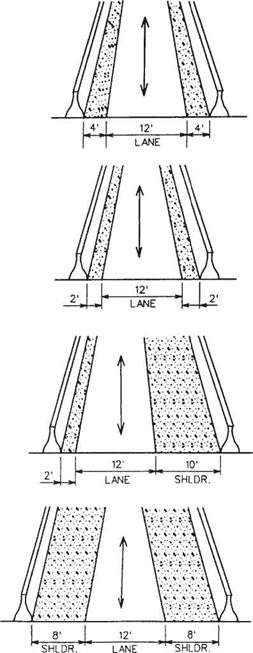
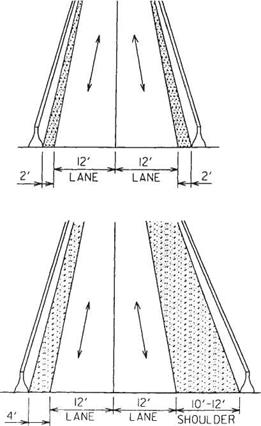
 Flexible Posts or
Flexible Posts or