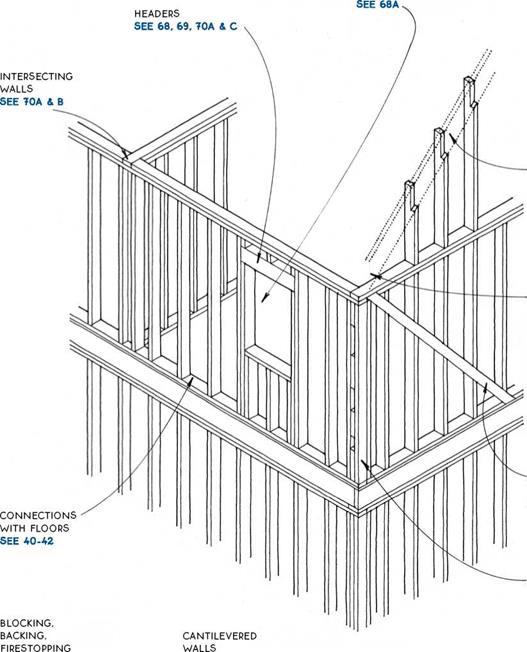
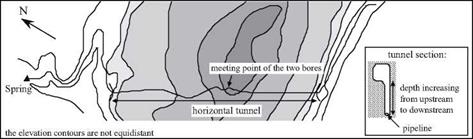
Summary of the Method
The determination of air voids based on compacted Marshall samples has been regarded in the Netherlands as the weakest point of the Dutch method of design. According to many engineers, these samples do not reflect the true arrangement of coarse aggregate particles in real pavement. Under real-world conditions, displacement of grains and their close arrangement occur as a result of the high temperature of the pavement and post-compaction; this may be followed by the reduction of air voids among the particles that create the skeleton. Then a significant decrease of air voids in the pavement can result, right up to a complete filling-up with mastic...
read more