SLIDING DOORS
 |
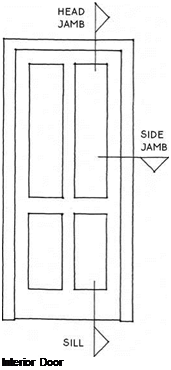 |
Because they do not have to be sealed against the weather, interior doors are much simpler than exterior doors. Interior doors are used primarily for privacy and to control air flow. The doors themselves are typically made of wood or composite wood products. They are 1% in. thick, and have either panels, like the one shown above, or a flush plywood veneer over a hollow core or solid core.
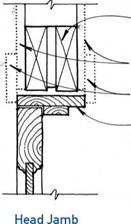
Hinged interior doors are usually prehung on a jamb without casings. The jamb on the hinged side is first nailed to the frame of the building, using shims to make it plumb. The jambs at the head and opposite side are then shimmed for proper clearance and nailed.
Some doors are hinged to a split jamb that will expand to accommodate some variation in wall thickness...
read more




