STEP 6 INSTALL THE SIDING PANELS
Thanks to the work you did in the previous step, panel installation can go quickly, especially when you have a good-size crew, as we did on this job. The first panel course is always the bottom-most course. Start against the corner on one side of the house (preferably the back corner). Pull up the first panel, snap it into the starter strip, and slide the end of the panel under the corner trim’s top edge. Keep the panel seated in the starter strip as you drive nails into each stud. The nail heads should be Мб in. proud of the flange. Don’t drive nails at the edge of a slot or through the vinyl itself. If the prepunched slot is not centered over a stud, lengthen the slot with a utility knife or a slot-punch tool.


 Once the panel is nailed in position, check whether you can slide it bac...
Once the panel is nailed in position, check whether you can slide it bac...







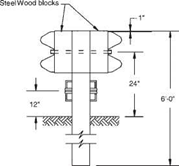

 A long, flat work surface is essential for vinyl siding and sheet-metal work. A couple of 2×12 boards on sawhorses work fine. For precise 90- degree-angle cuts and angled rake cuts, I suggest making a cutting jig for a circular saw (see the bottom center photo).The jig, which sits on a long worktable, is essentially a wooden cradle that guides the base of the circular saw. The cradle can be positioned at a right angle, or at other angles, to the siding.
A long, flat work surface is essential for vinyl siding and sheet-metal work. A couple of 2×12 boards on sawhorses work fine. For precise 90- degree-angle cuts and angled rake cuts, I suggest making a cutting jig for a circular saw (see the bottom center photo).The jig, which sits on a long worktable, is essentially a wooden cradle that guides the base of the circular saw. The cradle can be positioned at a right angle, or at other angles, to the siding.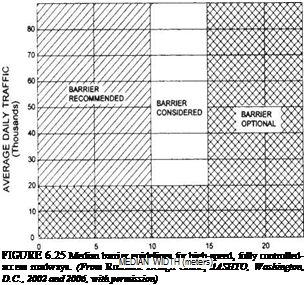
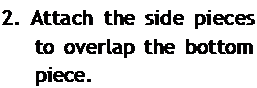
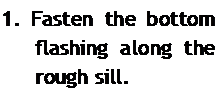
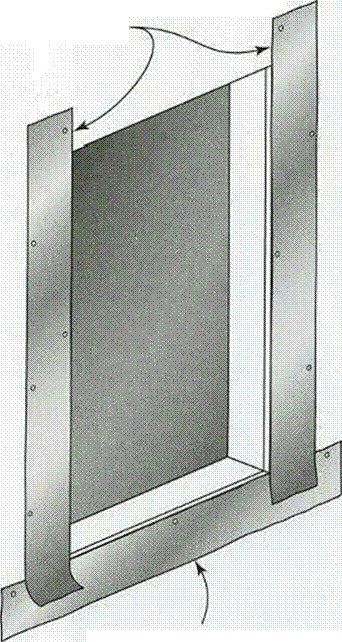

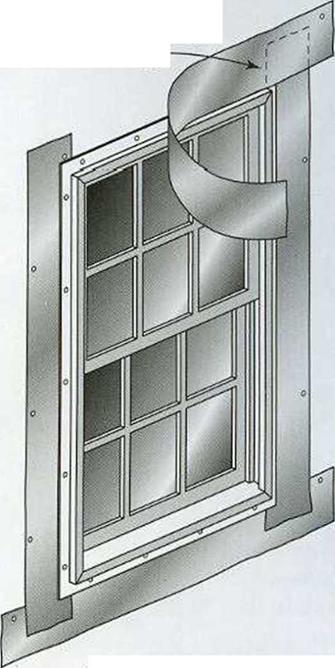
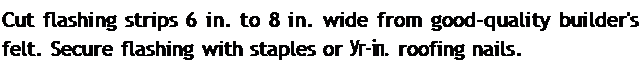 is used, you can still install a top piece of flashing. Cut a horizontal slit in the house – wrap above the window, then slip the top edge of the top flashing piece into the slit.
is used, you can still install a top piece of flashing. Cut a horizontal slit in the house – wrap above the window, then slip the top edge of the top flashing piece into the slit.