UPGRADING ROADSIDE BARRIER SYSTEMS
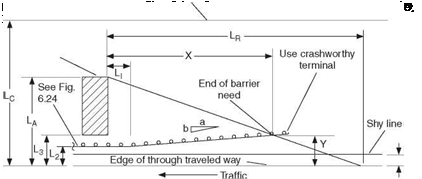
Table 6.6 provides a checklist that can be used to review existing barrier installations and determine adequacy for either structural or functional (design or placement) causes. Factors to be considered in determining the scope and extent of upgrading include the nature and extent of the deficiency, past accident history, and the cost-effectiveness of the recommended improvement. Remember to always consider the cost-effectiveness of eliminating or relocating the shielded feature.
Longitudinal median barriers are used to separate opposing traffic on divided highways, to separate local and through traffic, or to separate traffic in designated lanes...
read more