The basic principles to model the complete time-dependent heat transfer in soils are described in this section. More details of these and the associated effects can be
found in some of the better or more specialist geotechnical textbooks, for example Mitchell and Soga (2005) or Fredlund and Rahardjo (1993).
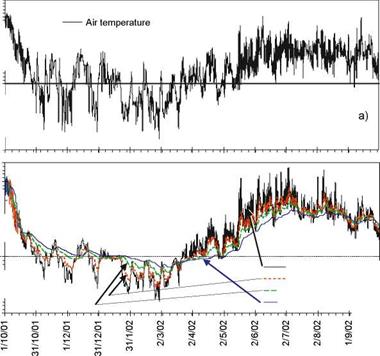
The water content in various road structures and the underlying soil are subject to climatic (temperature) effects. An example of the thermal variation in a road structure is given in Fig. 4.1. It can be clearly seen that the thermal state is definitely changing, which means that it is characterised by the heat transfer properties of the material. Temperatures may be positive or negative (inducing freezing). Heat transfer in soils is due to conduction, radiation, convection and vapour diffusion. A general overview of thermal transfer may be found in many textbooks, e. g. Selvadurai (2000) or Lewis and Schrefler (1998).
As pavement surface temperature depends greatly on the weather, typically changing hourly and daily, the physical process never reaches a steady state (i. e. there would be only a long-term equilibrium).
Geostructures, like road pavements and embankments, are made up of porous materials with solid and fluid phases. At micro-scale, i. e. the grains and pores scale, the heat transfer is highly complex, involving convection and radiation in the pores
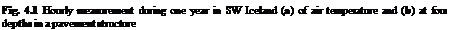
 25
25
20
15
10
-10
-15
-20
25
20
15
10
5
0
-5
-10
-15
and conduction in the grains. At the engineering scale (i. e. at macro-scale, at the layers thickness scale), the solid, liquid and gas phases may be considered separately as a continuum.
As discussed by Selvadurai (2000), it is known by experience that heat flows from points of higher temperature to points of lower temperature. Heat is, therefore, a form of energy, which is released by warmer regions of a body to the cooler regions.
Although heat flow cannot be measured directly, its presence manifests itself in terms of a measurable scalar quantity, which is the temperature. From the knowledge of the temperature distribution T(x, t) within a region, it is possible to calculate the heat flow within the region. As a consequence, the major part of the study of heat transfer in geostructures focuses on the determination of the temperature distribution within the medium which is subjected to appropriate boundary conditions and initial conditions applicable to T (x, t).
4.2.1 Conduction
Conduction refers to the mode of heat transfer where this energy transport takes place in the solid phase of the porous media and fluids, which are at rest. This is in contrast to convective heat transfer, which involves motion of a conducting fluid.
The grains of a soil, typically, are in contact with each other at distinct contact points and pores between grains are filled with a mixture of air and water. When completely dry the heat flow passes mainly through the grains, but has to bridge the air-filled gaps around the contact points. At very low water contents, thin adsorbed water layers cover the grains. The thickness of these layers increases with increasing water content as introduced in Chapter 2. At higher water contents, rings of liquid water form around the contact points between the grains. From this point on, the thermal conductivity increases rapidly with increasing water content. At even higher water contents, complete pores are filled with water resulting in a further but slower increase in thermal conductivity.
For a conducting medium which possesses homogeneity and isotropy with respect to its heat conduction characteristics (all parameters which govern the heat conduction process are assumed to be independent of direction and position), it is assumed that the amount of heat crossing an element of material in a given time, At, is proportional to the difference in temperature, T, and related to the material properties. Generalizing this concept leads to Fourier’s equation that defines a vector of heat flow Q (W/m2):
Q = – XV T = – XgradT (4.1)
where X(W/m°C) is defined as the thermal conductivity of the medium (see Section 4.3). Normally, the thermal conductivity of grains is in the range of 1-3 W/m°C. Water has a thermal conductivity of about 0.6 W/m°C at room temperature. In comparison with solids and liquids, the thermal conductivity of air is very small, being about 0.025 W/m°C.
For anisotropic materials like soils, Eq. 4.1 is generalized in matrix form:
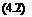 Q = – A. V T = – XgradT
Q = – A. V T = – XgradT
where X is the matrix of thermal conductivities.






 25
25