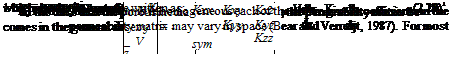Drainability
Broadly graded aggregates, as typically used in granular base and sub-base layers of the road construction have relatively small pores as the large pores between the coarser particles are mostly filled with smaller particles. This means that coefficient of permeability values, as characterised by the Darcy coefficient, K, are relatively low. Laboratory testing of typical sub-base aggregates has revealed hydraulic conductivity values that are usually less than 10-3 m/s in the unlikely even of saturation (Jones and Jones, 1989) and as low as an effective value of 10-6 m/s when, more normally, in a partially saturated state.
 |
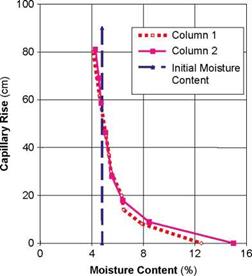 |
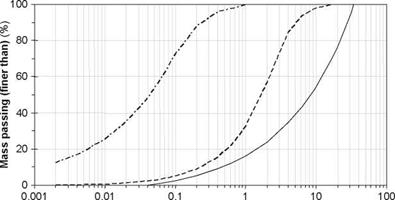
A second implication is that the pores will have a measurable suction ability. Hence dryer aggregates will usually show an ability to pull water towards them. There is a draft CEN standard (1999) for the evaluation of the suction height (i. e. of matric potential which is an indirect measure of the suction capacity of the aggregate). Figure 2.12 shows a result obtained by a similar method in which a column of
Measurement Techniques for Water Flow
SigurSur Erlingsson[4], Susanne Baltzer, Jose Baena and Gunnar Bjarnason
Abstract The chapter describes different measurement techniques for water-flow – related phenomena in pavements and embankments, i. e. water content, permeability and suction. For estimating the water content the gravimetric method is described as well as non-destructive methods such as neutron scattering, time domain reflectom – etry and ground penetrating radar. Then methods for estimating both the saturated and the unsaturated permeability of soils and granular materials are described. Both steady-state and unsteady methods are mentioned. Finally, common methods for measuring soil suction are briefly introduced.
Keywords Water flow ■ measurements ■ water content ■ permeability ■ suction
Water entering a pavement structure migrates as moisture through the structure. The amount of water penetrating the pavement is dependent on precipitation, drainage, design of the road structure, type and condition of the surface layer (cracks, joints) and shoulders and the materials in the pavement, subgrade and subsoil. Seasonal fluctuations in temperature, i. e. freezing and thawing, can also provoke moisture flow inside the pavement structure. An excess of water can cause a lower bearing capacity of the pavement structure and reduces pavement life (see Chapters 8 and 10). Also of concern is transport of contaminants with the liquid fluxes from the road and into the environment (see Chapter 6). As pavement deterioration can be reduced by proper drainage it is important to be able to measure the water content in order to understand how water moves within the road structure.
Predictions of water flow and contaminant transport in unsaturated soils should be based on an accurate description of the subsurface conditions including the aggregates
and hydrological properties of the materials involved. Therefore measurements of the fundamental parameters regarding flux of water need to be carried out. This also helps to set the initial conditions for analysis in water flow modelling.
The most important parameters related to the movement of water through pavement structures are the quantity and spatial distributions of moisture inside the pavement, the coefficient of permeability of individual layers and their matric suctions. These parameters can be determined experimentally, either in the field or in the laboratory, by various techniques. The most common of these methods used in road engineering will be briefly described in this chapter.






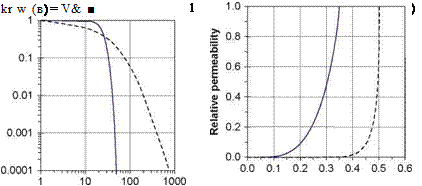
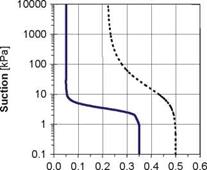
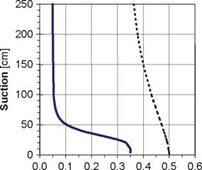
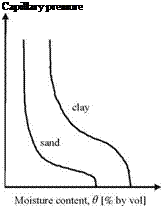
![The Soil Water Characteristic Curve (SWCC) Подпись: Capillary pressure Moisture content, 0 [% by vol]](/img/1312/image070_4.gif)
 у
у