Porous Asphalt
In countries that suffer from large amounts of rainfall, the asphaltic wearing surfaces are often constructed of open graded asphaltic mixtures. The high permeability of these wearing surfaces ensures a fast drainage of the water away from
|
Fig. 5.15 (a) bad road visibility conditions (b) hydroplaning and ‘splash and spray’ (Erkens, 2005). Reproduced by permission of N. Kringos |
the surface, avoiding hydroplaning and bad visibility conditions due to ‘splash and spray’, Fig. 5.15, and thus improving the overall road safety.
Porous asphalt uses aggregate with a moderate to coarse median particle size and a very steep grading curve – i. e. the majority of the stones in the mixture are of a similar size. This has the effect of developing a mixture with a very high air void volume (20-30%) with stones only adhering to each other by virtue of the films of bitumen at their point of contact. In this way its porosity is very high compared with conventional asphaltic material and water does not easily collect on the surface during rainstorms.
An added benefit not included in the original concept, but now an important driving force for the wider adoption of porous asphalt surfacings is the reduced traffic noise from pavements with these surfacings. The porous nature reduces tyre-surface interaction sounds and acts as a partial absorbent of other vehicle induced noise. Typically they provides a 3-5 dB(A) noise reduction over conventional pavement surfacings. Even greater benefits can be achieved by using two-layer porous asphalt with a finer, filter, layer over a coarser, drainage layer. Noise reduction may then be 8 or 9 dB(A) quieter than conventional asphaltic mixtures and 4 dB(A) quieter than a single-layer porous asphalt.
As the surfacing is so permeable, rain can drain vertically into the porous asphalt layer before being conveyed laterally within the pavement. Typically a porous asphalt surfacing will have a thickness of between 20 and 100 mm and be placed on top of an impermeable asphaltic base. Hence, water flowing in the surfacing cannot continue to flow vertically but is forced to travel sideways, exiting from the layer at its edge. Unless this edge is free, special attention must be paid as to how the water is to be collected and led away from the pavement. An impermeable edge, such as a conventional kerb, would dam the water within the layer. Consequently special kerbs with inlets and pipe systems have been developed to lead the water into a conventional surface drainage system (Highways Agency, 1997).
Despite the advantages of the material in providing relatively dry surfaces in wet weather, the material and its use pose a number of problems:
1. Lack of durability. Careful mixture design is needed to ensure that there is enough bitumen to coat the stones and ensure longevity of performance – too much and the mixture may rut too readily and the pores become blocked by bitumen (preventing drainage). Too little bitumen and ravelling will be likely (as described in Section 5.5.1), particularly in cold weather when ice could form in the pore space forcing the topmost layers of stone loose. An added issue is that the greater opportunity for bitumen to react with atmospheric oxygen, because of air in the voids, tends to lead to early embrittlement of the bitumen (Herrington et al., 2005). Bitumen film thickness is, thus, of particular importance. Hence, both design and construction practice require careful attention, perhaps more so than for conventional asphaltic mixtures. More detailed coverage of this topic is beyond the scope of this chapter, but interested readers may wish to consult NAPA (2004).
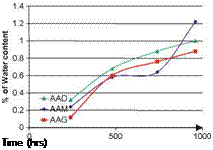
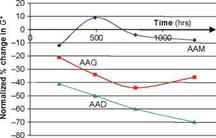
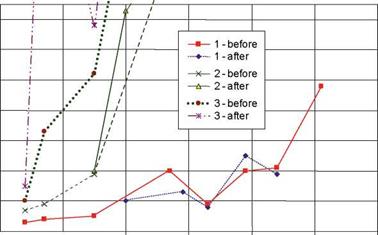
2. Clogging due to ingress of particulates. Small particles and dust, that comes from the environment, blown soil, engine wear, brake wear and from cargoes (see Chapter 6, Section 6.2), tend to get washed into the pore space of the porous asphalt, thereby blocking it. In thin porous surfacings on high-speed roads it appears that reduction in permeability is not of great concern. After some initial deterioration, further clogging is often not significant, probably because high-speed traffic develops high transient water pulses in the pores of the asphaltic mixture during wet weather, causing a self-cleansing action (Bendtsen et al., 2005). In slower speed roads this action is not evident and clogging is, typically, progressive. These authors monitored an urban test road in Denmark comprising 3 porous asphaltic surfacings and a control surface (Table 5.6).
Using an infiltrometer somewhat like that of Cooley (1999), see Section 5.4.1, Bendtsen et al. (2005) observed, Fig. 5.16, that clogging developed quite rapidly in the finer asphaltic pavements. The two porous pavements with 5 mm aggregate, Sections II and III, were effectively clogged after 15-20 months whereas Pavement I with 8 mm aggregate remained in a much better condition. The reason for this clogging is believed to be the dirt and fine material from the adjacent dense asphaltic concrete pavement being dragged onto the porous pavements by vehicle tyres, since clogging first appeared at the position nearest to the reference section.
|
Table 5.6 Danish test road construction (after Bendtsen et al., 2005)
|
70
![]()
 «Г
«Г
I 60
E
50
40
30
о
£ 20
о
 |
E [11]
3. Cold weather clogging by ice and snow. BackstrOm and BergstrOm (2000) evaluated the function of porous asphalt in cold climates using a climate room. At the point of freezing point, the infiltration capacity of porous asphalt was approximately 50% of the infiltration capacity at +20°C. They simulated conditions of snowmelt by exposing the porous asphalt to alternating melting and freezing over a period of 2 days and found that the infiltration capacity was reduced by approximately 90%.
To overcome clogging, cleaning devices have been developed. These (Figs. 5.17 and 5.18) typically comprise high pressure water jets that aim to disturb and erode fines resting in the pores of the porous asphalt, washing them to the surface from where they may be vacuum-collected by the cleansing machine. It is interesting to note that the results of Bendtsen et al. (Fig. 5.16) show that there is not a significant reduction in the level of clogging due to cleaning (compare ‘before’ (b) to ‘after’ (a) readings in the figure) and that cleaning did not bring back performance close to the original function.
|
Fig. 5.18 Porous asphalt cleaning machine and diagram of active part. Reproduced by permission of Sakai Heavy Industries |
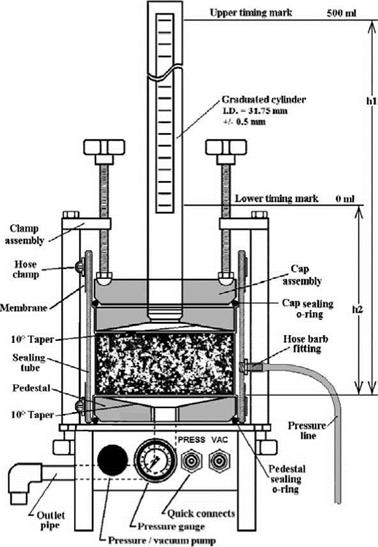
A range of equipment exits to determine permeability of asphaltic mixtures both by in-situ and laboratory testing. At present the values of permeability collected seem, mostly, to be being used for relative performance assessments and they are not much integrated in whole-pavement water regime modelling. Current advances in computational engineering and mechanical and physio-chemical testing enable the identification of the actual physical processes of water-induced damage in asphaltic mixtures and the evaluation of their effects on the total mixture response. It is hoped that, over a period of time, availability of these resources will enable a gradual transition in mixture design from a design-by-testing approach to an approach in which design is by identification of the optimal choice of individual mixture components on the basis of their physio-chemical and mechanical characteristics and interactions. The increasing use of porous asphalt for noise reduction and spray reduction purposes is an important challenge to the pavement engineer. Purposely allowing water into the structure provides the opportunity for much greater and faster ravelling. There are also concerns about clogging due to washed-in fines and due to ice formation. Rehabilitating clogged porous asphalt without causing premature damage is a challenge.
Acknowledgments Some of the work described in this chapter has been performed with financial, computational or experimental support of Ooms Nederland Holding Bv, the Section of Structural Mechanics of TU-Delft (both in the Netherlands) and the Turner Fairbanks Highway Research Center of the US Federal Highway Administration. The authors wish, therefore, to express their thanks to Dr. A. de Bondt, ir. C. Kasbergen and Dr. J. Youtcheff respectively for this.








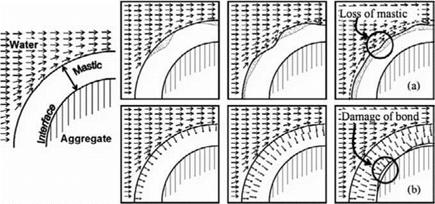
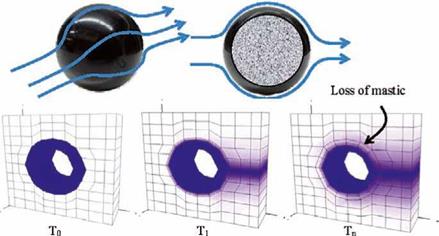
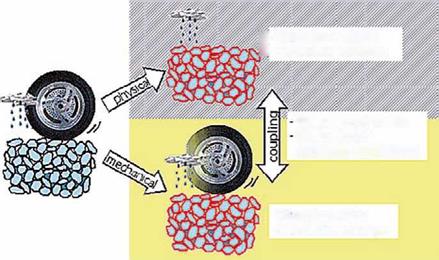 p – Moisture diffusion Ш -»Advective transport
p – Moisture diffusion Ш -»Advective transport