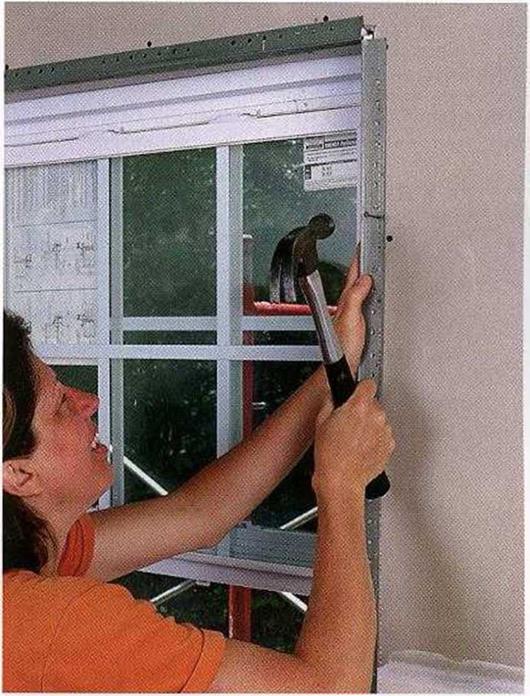
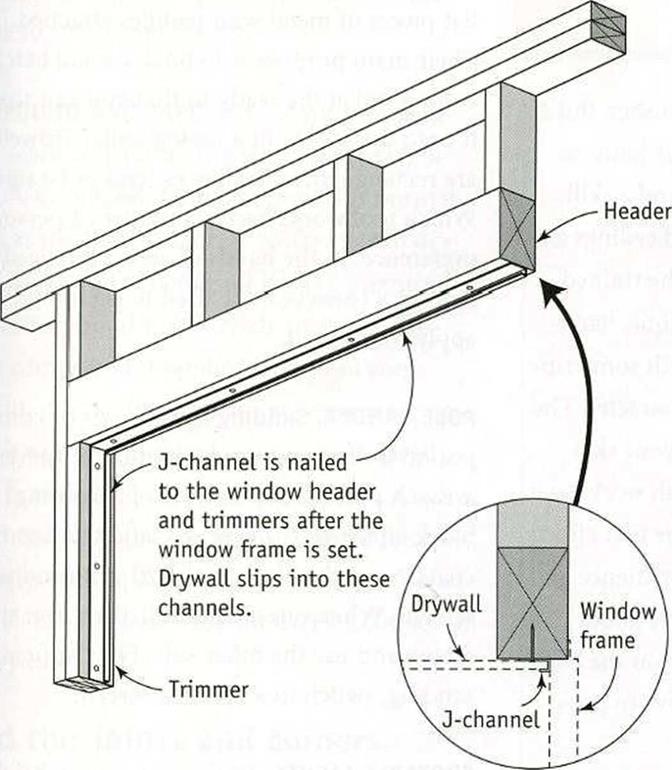
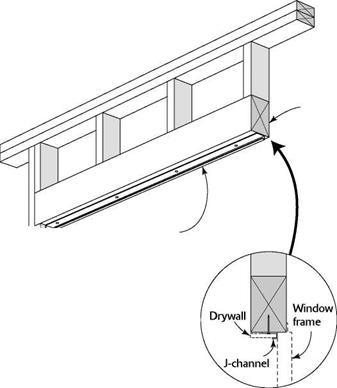
PITCH-CHANGE FLASHING
![]()
 wall sheathing on framing of wood flue
wall sheathing on framing of wood flue
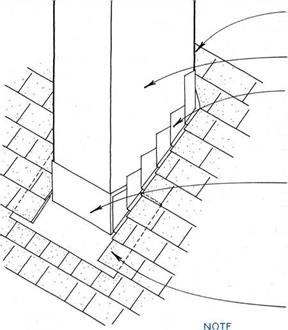
STEp FLASHiNG WOVEN WITH ROOFiNG COuRSES
(shown before it is lapped with moisture barrier & SIDING), SEE 171C,
OR
ALTERNATIVE SIDEWALL FLASHiNG, SEE 171B.
BASE FLASHiNG WRApS CORNERS, ExTENDS uNDER SHINGLES AT SIDES 4 IN. (MIN.) & LApS SHINGLES AT BASE 4 IN. (MIN.)
OR
ALTERNATIVE OuTSIDE CORNER FLASHiNG AT BOTH CORNERS, SEE 172A,
COMBINED WITH ABuTTiNG ROOF FLASHiNG,
SEE 169D.
 |
 |
The flashing for a masonry chimney is best made of permanent materials such as copper or stainless steel. The flashing fits to the roof using the same principles as flashing for wood-framed flues (see 173B). The top edge of this flashing is then lapped with a counterflashing that is set into the mortar joints between masonry units...
read more