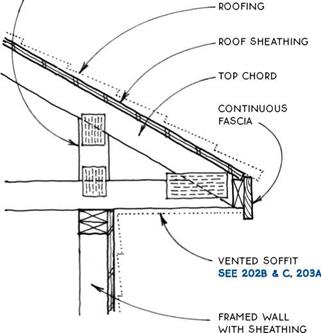
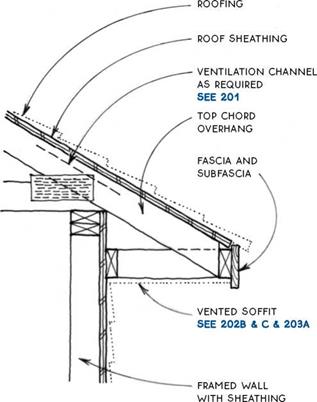
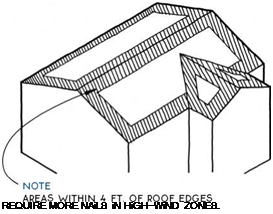
Checking the Building for Level
Using a transit or laser is the best way to check for level. A water level can also be used. Once a level foundation has been established, you are ready to cut, drill, and set the mudsill in place.
The foundation and/or slab should be ready for you to start framing when you first arrive. Sometimes, however, this is not the case, and time will be needed to “shoot" (measure using a transit or laser) a foundation and slab. Time must also be allotted to fix any problems in the concrete. It will be your responsibility to check and make a suggestion if you think corrective work is necessary. Start by checking and recording your findings. Record your findings in a way that lets you use the information if you decide the concrete needs corrective work...
read more