Jacking and Shoring
Jacking refers to raising or lowering a building so you can repair or replace defective framing or failed foundations or to level a house that has settled excessively. Shoring refers to a temporary system of posts, beams, and other structural elements that support building loads. Temporary is the crucial word: Shoring supports the building between jackings. Once repairs are complete, you need to lower the house and remove the shoring as soon as possible. If repairs are extensive—say, replacing foundation sections—have a structural engineer design the new sections; specify jack size; and specify the posts, beams, and bracing needed to safely jack and shore the building.
Jacking a house is nerve-wracking...
read more








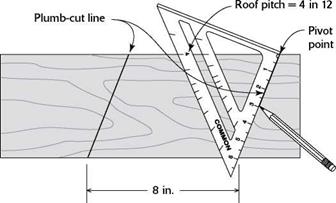
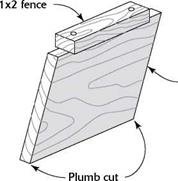
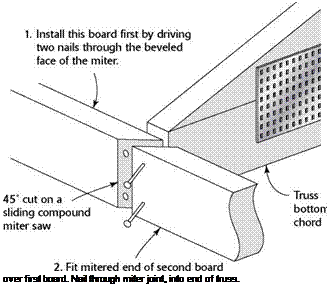 boards are less demanding...
boards are less demanding...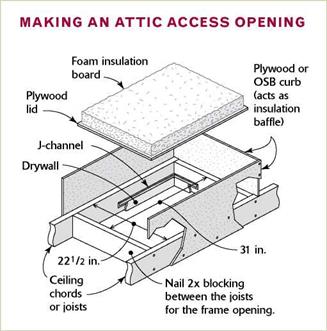
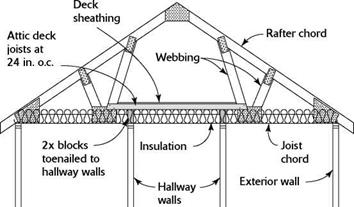

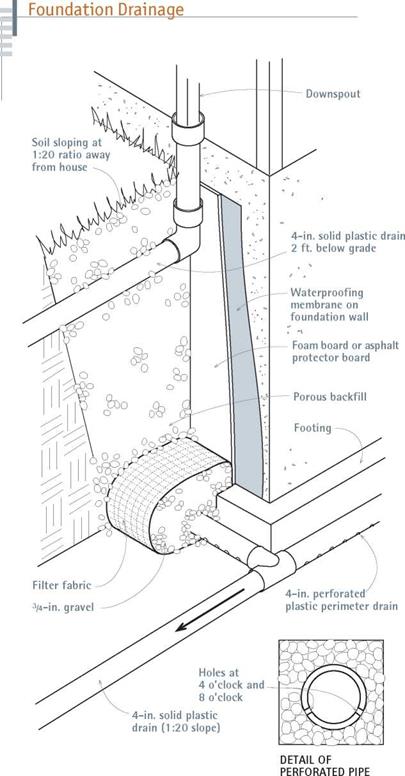
 Foundation issues
Foundation issues a barge rafter meets a gutter or fascia board, which extends along the eave and is fastened to the ends of the rafter tails.
a barge rafter meets a gutter or fascia board, which extends along the eave and is fastened to the ends of the rafter tails.