A comparison of macrotexture depths of courses executed with various asphalt mixtures has been presented in an Australian paper (Oliver, 2001):
• Surface dressing (greater than 10 mm)—macrotexture less than 1.5 mm
• AC (greater than 10 mm)—macrotexture 0.4 to 0.8 mm
• Porous asphalt—macrotexture less than 1.2 mm
• SMA—macrotexture less than 0.7 mm
• Slurry seal—macrotexture 0.4-0.8 mm
• Cement concrete (brushed)—macrotexture 0.2-0.7 mm
Changes in some SMA characteristics occurring over time have been indicated in various investigations. In the United Kingdom, Richardson (1997) described changes in the SMA macrotexture during the months following the construction of a course. The SMA macrotexture, just after placement, was initially at a level of 1.5-1.6 mm. Then it gradually reduced to 1.1 mm after 21 months. It should be added that the reported results applied to an SMA with a gradation that was used in the United Kingdom to achieve a required high macrotexture after placement (see Chapter 10). The applied gradation was characterized by a gradation curve below the typical gradation limits according to German guidelines (see comparison of curves in Chapter 14, Figures 14.2 through 14.5).
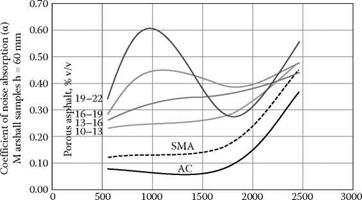
It should be noted that gritting used to enhance SMA antiskidding properties has additional consequences, especially in the first period after execution, namely a slight decrease in the surface macrotexture. Grit particles (and the remains of them crushed by rollers) gather in spaces among SMA coarse aggregates and only some time after the opening of a road to traffic are they pulled up (sucked out) by vehicle tires and scattered across the shoulder or median (Richardson, 1997). So just after gritting, macrotexture may be low (see Figure 12.6b), it but will eventually improve.
Argentinean investigations (Bolzan, 2002) conducted just after a highway modernization project, including the placement of a new SMA 0/19 course, showed it provided high macrotexture 2.2 mm deep (measured by the sand patch method). At another section of SMA 0/12 mm, the macrotexture depth amounted to only 1.4-1.7 mm.
In Germany Behle et al. (2005) conducted research into the relationship between PSV and final skid-resistance of an SMA layer. The authors presented the results of measurements with a sideways coefficient routine investigation machine (SCRIM) over a period of 4.5 years and a concept for calculating the PSV of mixed aggregates with different individual PSVs by weighted average.
By and large, based on straightforward experiments and a series of results, the following general technological recommendations to improve the antiskidding properties of SMA wearing courses may be put forward:
• Apply mixtures with a lower maximum aggregate size (more contact points between the SMA and tire).
• Consider microtexture—prefer aggregates with a high PSV index (low polishing susceptibility) and aggregate mixtures of various rocks with various wear rates; if possible, also use artificial aggregates (slags).
• Consider macrotexture—avoid factors that increase the risk of squeezing mastic out on a surface such as mixtures with an insufficient content of voids and or those susceptible to compaction under traffic; for the same reason do not use pneumatic rollers and use vibratory rolling with caution.
• Apply grit to make the surface rough by spreading the grit evenly, followed by rolling while the surface is hot enough.
• Open the lane to traffic only after the SMA has finally cooled off.