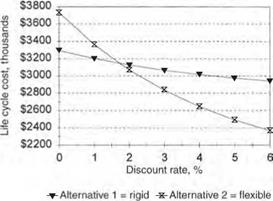
Once a pavement is determined to have unacceptable smoothness or has lost its ability to properly transport goods, it is reasonable to determine the best strategy to return the pavement to its original intended function. Many of the decisions that define the point where corrective action should be taken are management decisions and can be addressed properly only in a comprehensive study of pavement management data. Many considerations must be addressed before determining a list of good rehabilitation options. Leading rehabilitation techniques are reviewed in the following articles.
3.9.1 Rehabilitation of Rigid Pavement
CPR. The most common method of restoration for jointed pavement, both reinforced and nonreinforced, is termed concrete pavement restoration (CPR). CPR includes load transfer, restoration, joint removal and replacement, construction of rigid shoulders (if not already present), profile grinding to reestablish smoothness, and usually resealing joints and sealing any cracks. The CPR technique is only used when nondestructive testing measurements indicate that an asphalt overlay is not needed for the future
|
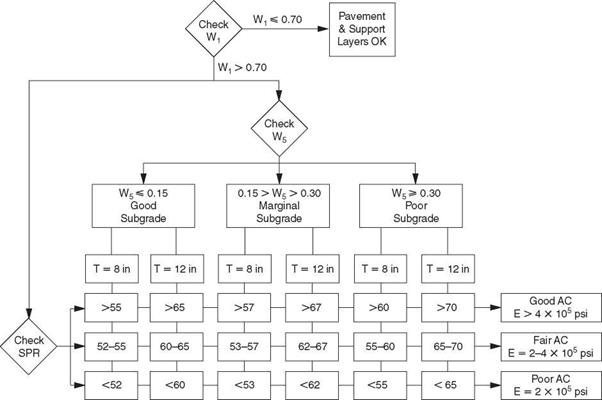
FIGURE 3.52 Evaluation of thick (thickness 8 to 12 in or 200 to 300 mm) flexible pavements from Dynaflect measurements. Conversion: 1 psi = 6.895 X 10-3 MPa. (From К. Majidzadeh and V. Kumar, Manual of Operation and Use of Dynaflect for Pavement Evaluation, Resource International, Inc., Columbus, Ohio, Report No. FHWA/OH-83/004, October 1983, with permission)
|
|
 |
|
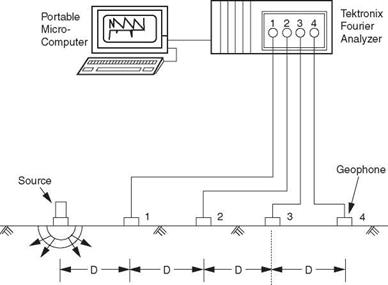
FIGURE 3.53 Schematic diagram of spectral analysis of surface waves (SASW) testing setup. (From S. Nazarian, D. Yuan, and M. R. Baker, Rapid Determination of Moduli with Spectral-Analysis-of-Surface-Waves Method, The University of Texas at El Paso, El Paso, Texas, Report No. TX-94 1243-1, November 1995, with permission)
|
design traffic. The disadvantage of this type of treatment is that, if the joints are not repaired properly, they will fail prematurely. Joint repair quantities are difficult to estimate, because joints continue to fail between the time the rehabilitation was designed and the time construction begins. The advantage of this type of treatment is that it utilizes the strength of existing pavement rather than an overlay, so overhead clearance problems are postponed or eliminated.
Repair and Overlay. When nondestructive testing measurements indicate that the existing slab thickness is insufficient to carry future design traffic, a common technique is to repair failed joints or pavement and add an asphalt overlay. Generally, rigid repairs are preferred over flexible repairs. Flexible repairs in a rigid pavement do nothing to reestablish load transfer across the failed joint. Flexible repairs also have a tendency to heave because they are weak in compression and the rigid pavements expand during hot weather. Flexible repairs allow joints to open up beyond the design of the joint sealant, causing the joint sealant to fail. Finally, flexible repairs reduce pressure in a pavement and allow midpanel cracks to open up and lose aggregate interlock. The advantages of flexible repairs are the favorable cost and construction time. Disadvantages of rigid repairs include the construction complexity and time. It is important to realize that the biggest drawback of the repair and overlay strategy is the inability to estimate the amount of repair required at each pavement failure and, for jointed pavements, the number of joints that need repair. Designed overlays are usually thin (3 to 6 in or 75 to 150 mm). In cold climates, joints usually reflect through the overlay after one or two winters. Joint reflection cracking can be addressed by sawing and sealing a joint in the asphalt overlay at the exact same location as the joint in the underlying rigid pavement. Failure to align the flexible joint with the rigid joint will result in premature joint spalling of the asphalt layer.
Bonded Concrete Overlay. Another technique to increase pavement structural capacity is to bond additional concrete to the surface of the existing concrete pavement. The required overlay thickness is determined by subtracting the effective thickness, determined by nondestructive testing of the pavement, from the thickness required for a new pavement. Cracks in the underlying pavement will reflect through the overlay. Therefore, all joints and working cracks must be established in the overlay directly over joints and cracks in the existing pavement. For CRC pavement, this is generally not a concern. The existing pavement must be cleaned to ensure a proper bond. This technique is advised only for pavements that are in sound condition with little distress. Any areas showing deterioration must be repaired prior to the overlay.
Break and Seat for JRCP. The break and seat method for jointed reinforced concrete
pavement is accomplished by breaking the long slabs into shorter slabs to distribute the expansion and contraction movement of the pavement over more cracks or joints. This reduces the strains in the asphalt overlay over the cracks or joints to the point where reflective cracking is retarded. The smaller slabs are seated in the subgrade by rolling to reduce vertical deflections. The overlay is designed as a new flexible pavement section with the broken and seated pavement as a base. The broken and seated pavement is given a structural coefficient as determined by nondestructive testing. One disadvantage of this technique is that, to fail or debond the reinforcing steel, tremendous breaking effort is required, and this results in a weak and nonuniform base. Where the reinforcing steel is not failed or debonded, large slabs continue to behave as large slabs, causing the joints to reflect through the overlay. Additionally, breaking does not correct problems at joints. Failed joints continue to be weak points in the pavement and usually heave, creating a hump in the overlay. The advantage to this technique is that broken and seated pavements tend to require thick overlays and maintain a high level of serviceability. Additionally, reflective cracking is of low severity when compared with cracking in thin asphalt overlays.
Crack and Seat for JPCP. The crack and seat method for plain concrete pavement (nonreinforced) is accomplished by producing several transverse cracks in each slab, thus transforming the long slabs into shorter slabs to distribute the expansion and contraction movement. This reduces the strains in the asphalt overlay over the joints to the point where reflective cracking is retarded, and the smaller slabs are seated in the subgrade to reduce vertical deflections. By definition, crack and seat produces a crack visible when the pavement is wetted with water. As with break and seat, the overlay is designed as a new flexible pavement section with the cracked and seated pavement as a base, and with a structural coefficient as determined by nondestructive testing. The disadvantage of this method is that the cracking does not correct problems at joints. Joints that have failed continue to be weak points in the pavement and usually heave, creating a hump in the overlay. The advantage of this method is that cracked and seated pavements with thick overlays (7 in or more) exhibit a high level of serviceability, and reflective cracking is of low severity when compared with cracking in thin asphalt overlays.
Rubblize and Roll. Rubblize and roll is applicable for all types of rigid pavement. This method is accomplished by breaking the existing pavement into 6 in (152 mm) size or less using a resonant beam breaker or multihead breaker. The rubblized concrete is compacted with a roller and used as a base for a new pavement. The overlay is designed as a new flexible pavement section with the rubblized and rolled pavement as a base. The rubblized pavement is given a structural coefficient based on nondestructive testing. One disadvantage of this technique is that rubblizing weakens the pavement and thereby increases the required overlay thickness. Areas with soft subgrade require removal of the pavement and undercutting; otherwise, the rubblization process cannot be achieved properly. The geometry of the equipment prohibits breaking near portable barriers used for traffic control. Another disadvantage of this technique is that, because the resulting overlay is thick, elevation transitions at bridges require pavement replacement. One advantage of this technique is the complete utilization of the existing pavement as a uniform base without discontinuities. For reinforced concrete pavement, the technique serves to completely debond the steel from the concrete.
Thick Asphalt Overlay with No Repairs. A thick asphalt overlay with no repairs is a quick and inexpensive rehabilitation strategy that can be used on any rigid pavement beyond economical repair. As the overlay thickness is increased, vertical deflection is decreased as a result of the increased structure. Horizontal movements in the slab are decreased because of lower temperature variations. This decreases the strain at the interface of the overlay and pavement, which retards reflective cracking. The overlay is designed as a new flexible pavement section with the existing pavement as a base. The existing pavement is given a structural coefficient based on deflection testing. A disadvantage of this strategy is that problems at joints are not corrected. Joints that have failed continue to be weak points in the pavement. Another disadvantage is that the thick overlay necessitates pavement replacement to make elevation transitions at bridges. The advantages of this strategy are the low initial cost and ease of construction. Reflective cracking is of low severity when compared with cracking in thin asphalt overlays.
Unbonded Concrete Overlay. The purpose of breaking the bond between the old pavement and the proposed overlay is to separate the distresses in the old pavement from the new concrete overlay. Thus, the concrete overlay can be treated as a separate pavement, and the existing distressed pavement as a uniform base. There is little benefit derived from repairing the existing pavement prior to placing the overlay, as the bondbreaker will provide uniform support and interface for the concrete overlay. The bond – breaker is placed as a thin (1- to 3-in) asphalt overlay on the existing pavement, and the concrete overlay is placed on the bondbreaker. The thickness required for the concrete overlay can be determined using the following modified version of an equation developed by the Army Corps of Engineers:
T = V(RT)2 – (ET)2 (3.8)
where T = the required thickness of the concrete overlay, in (mm)
RT = required thickness of new concrete pavement on the existing subgrade and for the anticipated truck loading, in (mm); the existing subgrade strength can be determined from original construction and design records or from nondestructive testing
ET = effective thickness of existing concrete pavement as determined by nondestructive testing, in (mm)
This technique is most efficient if the entire width of the roadway is available for overlay at the same time, but this makes maintenance of traffic difficult. However, the strength of the existing pavement is utilized, and the performance can be expected to be similar to that of a new pavement.