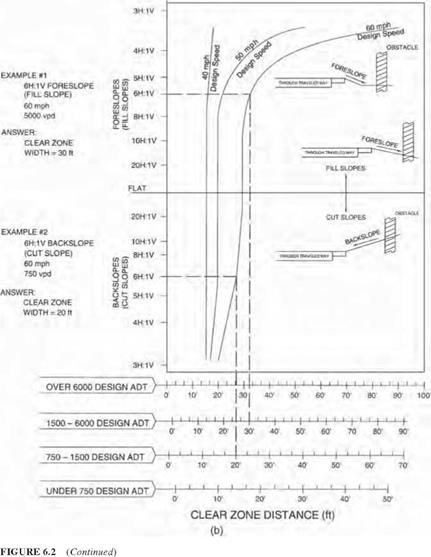
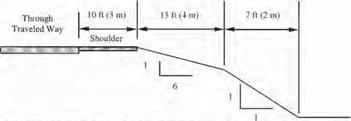
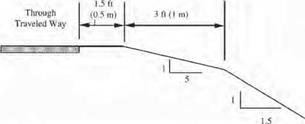
The drainage system should be designed, constructed, and maintained with considerations for both the hydraulic function and roadside safety. (See Chap. 5.) In addition to channels, elements of the system include curbs, cross-drainage (transverse) structures (pipes and culverts), parallel drainage structures, and drop inlets. The following three options, listed in order of preference, are applicable to each:
• Eliminate nonessential drainage structures.
• Design or modify drainage structures so they are traversable or present minimal hazard to errant vehicles.
• If relocation or redesign is impractical, shield with a traffic barrier if in a vulnerable location.
Curbs may be classified as vertical or sloping types. Vertical curbs, defined as those with vertical or nearly vertical faces, 6 in (150 mm) or more in height, discourage
a1:b1
motorists from leaving the highway. Sloping curbs have lower heights with sloping faces that can be easily traversed. Heights of 4 in (100 mm) or less are preferred for the latter to avoid dragging the underside of vehicles. Neither type of curb is desirable on high-speed highways, because either may cause overturning, particularly if the vehicle is spinning or slipping. In urban areas, a minimum horizontal clearance of 1.5 ft (0.5 m) beyond the face of the curb should be provided to obstacles. On high-speed roadways, curbs should not be used in front of traffic barriers, because unpredictable postimpact trajectories can result. If a curb must be used, locate it flush with the face of the railing
or behind it. Curb-barrier combinations for bridge railings should be crash-tested unless data are available.
Cross-drainage structures carry streams or drainage water transversely underneath the embankment. They may range in size from 18 in (450 mm) to 10 ft (3 m) or more, may be constructed of concrete, metal, or plastic (in some sizes), and may be furnished as round pipe, elliptical shapes, or boxes. Typically, inlets and outlets of larger structures have concrete headwalls and wingwalls, and those of smaller structures are beveled to match the slope. Pipe may also be furnished with square-cut ends. These designs may result in a
fixed object protruding above an embankment or an opening into which a vehicle can drop, causing an abrupt stop. Options available to minimize such obstacles include
• A traversable design
• Extension of the structure so it is less likely to be hit
• Shielding the structure
• Delineating the structure (when other measures are not feasible)
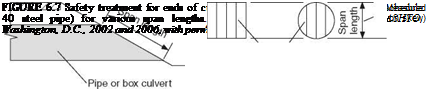
Traversable design. If a slope is generally traversable, the preferred treatment is to extend or shorten the structure and match the inlet or outlet shape to the embankment slope. Further treatment should not be required for small culverts, defined as a single pipe with a diameter of 36 in (900 mm) or less or multiple pipes with diameters of 30 in (750 mm) or less each. Single structures and end treatments wider than 3 ft (1 m) can be made traversable for passenger-size vehicles by using bar grates or pipes to reduce the clear opening width. To maintain hydraulic efficiency, it may be necessary to apply bar grates to flared wingwalls, flared end sections, or culvert extensions larger than the main barrel. Crash tests have shown that automobiles can cross grated culvert end sections on slopes as steep as 1:3, at speeds from 20 to 60 mi/h (30 to 100 km/h), when steel pipe on 30-in (750-mm) centers is used. This spacing does not significantly affect flow unless debris accumulates and causes clogging.
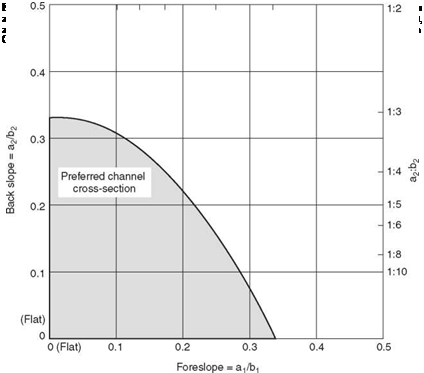
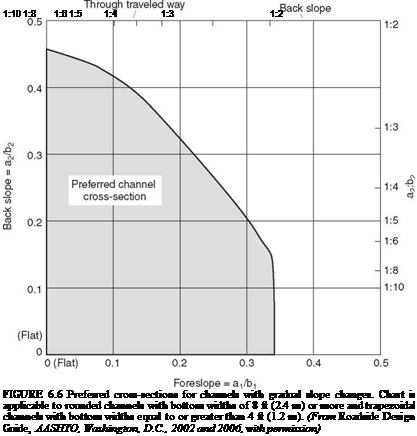
Design recommendations for safety treatment of culvert ends are summarized in Fig. 6.7. Where debris accumulation is not a concern and mowing operations are frequent, smaller openings may be tolerated and grates similar to those for drop inlets may be appropriate. In median areas, consider making culverts continuous and adding a median drainage inlet.
Extension of structure. For larger-sized drainage structures with inlets or outlets that cannot be readily made traversable, the structure can be extended so the obstacle is located at the edge or beyond the clear zone. This reduces but does not eliminate the possibility of hitting the pipe end. If the culvert headwall remains the only fixed object at the edge of the zone, simply extending the opening to the edge may not be the best solution. However, if there are numerous obstacles along the edge of the zone on the section under consideration, extension of the pipe might be an appropriate solution.
|
Span length, ft (m)
|
Inside diameter, in (mm)
|
|
3 (75)
|
|
Up to 12 (Up to 3.65)
|
3.5 (87)
|
|
12 to 16 (3.65 to 4.90)
|
4 (100)
|
|
16 to 20 (4.90 to 6.10)
|
3 (75)
|
|
20 (6.10 or less with center support)
|
Each 30 in max. (750 mm)

Section A-A
FIGURE 6.8 Safety treatment for drainage inlet or outlet. (From Roadside Design Guide, AASHTO, Washington, D. C., 2002 and 2006, with permission)
Shielding of structure. An appropriate traffic barrier should be considered for shielding a drainage structure that cannot be reasonably made traversable or extended outside the clear zone. Because the barrier will be closer to the roadway and longer than the obstacle, it is more likely to be hit. However, if properly designed, constructed, and maintained, the barrier should provide an increased level of safety.
Parallel drainage structures are those that are oriented parallel to the traffic flow to carry water under driveways, entrances, ramps, side roads, and median crossovers. Such structures may represent a significant hazard if they can be struck head on by an errant vehicle. Options for safety treatment are similar to those for cross-drainage structures. If entrances are closely spaced, consider converting the open channel into a closed storm drain, backfilling areas between entrances, and eliminating multiple obstacles. Research has shown that, for parallel drainage structures, wheel snagging can be significantly reduced with pipe grates oriented perpendicular to the traffic direction and having a spacing of 24 in (600 mm) or less. Single pipes of 24 in (600 mm) diameter or less generally do not require a grate, but multiple small pipes may require one. Figure 6.8 illustrates a design for the ends of a parallel culvert. In situations such as intersecting ramps, consider relocating the culvert farther back from the main road, out of the clear zone.
Drop inlets include on-roadway and off-roadway structures. On-roadway inlets, which are located along the shoulder to intercept surface runoff, include curb opening inlets, grated inlets, and slotted drains. If installed flush with the pavement, they do not cause a significant safety problem. Off-roadway drop inlets are used in medians of divided roadways or in roadside ditches. The hazard can be minimized by making the inlets flush with the drainage surface. Safety treatment should be such as to prevent a vehicle from dropping into the inlet, snagging, and losing control.







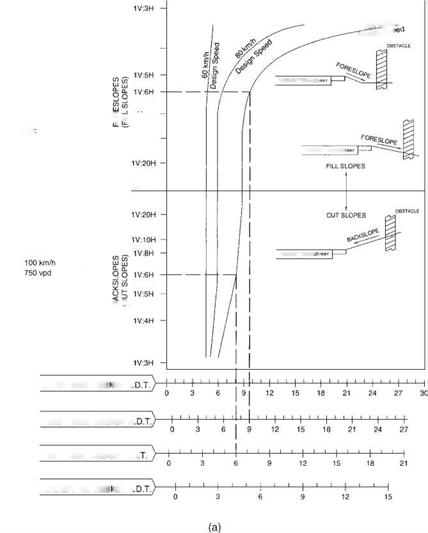 CLEAR-ZONE DISTANCE (m)
CLEAR-ZONE DISTANCE (m)