Drainability
Broadly graded aggregates, as typically used in granular base and sub-base layers of the road construction have relatively small pores as the large pores between the coarser particles are mostly filled with smaller particles. This means that coefficient of permeability values, as characterised by the Darcy coefficient, K, are relatively low. Laboratory testing of typical sub-base aggregates has revealed hydraulic conductivity values that are usually less than 10-3 m/s in the unlikely even of saturation (Jones and Jones, 1989) and as low as an effective value of 10-6 m/s when, more normally, in a partially saturated state.
 |
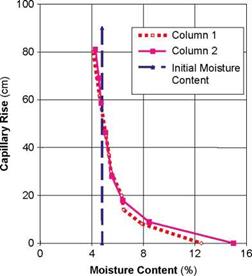 |
A second implication is that the pores will have a measurable suction ability...
read more





![STEP4 Attach the Sills Подпись: SNAP CHALKLINES TO LAY OUT THE SILL. The line shows where the sill's inside edge rests. If the foundation isn't perfectly square, adjust the line's position so that the sills will be. [Photo by Roe A. Osborn, courtesy Fine Homebuilding magazine, The Taunton Press, Inc.]](/img/1312/image214_1.gif)
 Most codes require that anchor bolts be located I ft. from each corner of the foundation, 1 ft. from the ends of each sill plate, and a maximum of 6 ft. o. c. everywhere else. These are minimum requirements. Builders living in earthquake or high-wind areas often use %-in.-dia...
Most codes require that anchor bolts be located I ft. from each corner of the foundation, 1 ft. from the ends of each sill plate, and a maximum of 6 ft. o. c. everywhere else. These are minimum requirements. Builders living in earthquake or high-wind areas often use %-in.-dia...