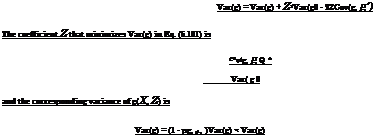The Stiffness Matrix
From Eq. 11.24, it appears that the stiffness matrix is a derivative of the internal forces:
|
n Fint n FLhK] = – F – = — *ljBLjdvj (11.25)
Fig. 11.2 Illustrative layout of stiffness matrix |
Two contributions will be obtained (Fig. 11.2). On the one hand, one has to derive the stress state with respect to the strain field, itself depending on the displacement field...
read more