Thermal expansion can occur in pipes when there are temperature fluctuations. Damage can result from this expansion if the pipe is not installed properly. In order to avoid damage, refer to Figures 11.7, 11.8, and 11.9 to learn about the tolerances needed for various types of pipe (Fig. 11.10).

|
Coefficient
|
Pipe material
|
in/in/°F
|
(°С)
|
|
Metallic pipe
|
|
Carbon steel
|
0.000005
|
(14.0)
|
|
Stainless steel
|
0.000115
|
(69)
|
|
Cast iron
|
0.0000056
|
(1.0)
|
|
Copper
|
0.000010
|
(1.8)
|
|
Aluminum
|
0.0000980
|
(1.7)
|
|
Brass (yellow)
|
0.000001
|
(1.8)
|
|
Brass (red)
|
0.000009
|
(1.4)
|
|
|
Plastic pipe
|
ABS
|
0.00005
|
(8)
|
|
PVC
|
0.000060
|
(33)
|
|
PB
|
0.000150
|
(72)
|
|
PE
|
0.000080
|
(14.4)
|
|
CPVC
|
0.000035
|
(6.3)
|
|
Styrene
|
0.000060
|
(33)
|
|
PVDF
|
0.000085
|
(14.5)
|
|
PP
|
0.000065
|
(77)
|
|
Saran
|
0.000038
|
(6.5)
|
|
CAB
|
0.000080
|
(14.4)
|
|
FRP (average)
|
0.000011
|
(1.9)
|
|
PVDF
|
0.000096
|
(15.1)
|
|
CAB
|
0.000085
|
(14.5)
|
|
HDPE
|
0.00011
|
(68)
|
|
Glass
|
|
Borosilicate
|
0.0000018
|
(0.33)
|
|
FIGURE 11.7 ■ Thermal expansion of piping materials. (Courtesy of McGraw-Hill)
|
Temperature Change (°F)
|
Length (ft)
|
40
|
50
|
60
|
70
|
80
|
90
|
100
|
|
20
|
0.278
|
0.348
|
0.418
|
0.487
|
0.557
|
0.626
|
0.696
|
|
40
|
0.557
|
0.696
|
0.835
|
0.974
|
1.114
|
1.235
|
1.392
|
|
60
|
0.835
|
1.044
|
1.253
|
1.462
|
1.670
|
1.879
|
2.088
|
|
80
|
1.134
|
1.392
|
1.670
|
1.879
|
2.227
|
2.506
|
2.784
|
|
100
|
1.192
|
1.740
|
2.088
|
2.436
|
2.784
|
3.132
|
3.480
|
|
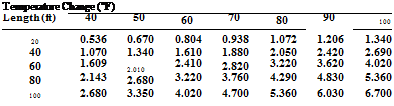
FIGURE 11.9 ■ Thermal expansion of all pipes (except PVC-DWV). (Courtesy of McGraw-Hill)
FIGURE 11.10 ■ Tech tips.







Leave a reply