SOME FACTS ABOUT COPPER PIPE AND TUBING
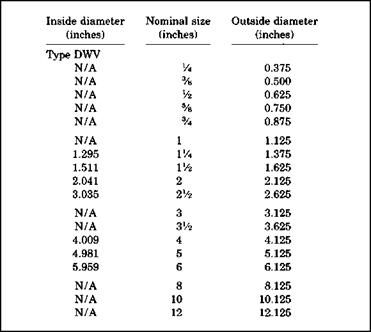
Would you like some facts about copper pipe and tubing? Well, you’re in the right place. Let’s go over some data that could serve you well in your plumbing endeavors. Figure 11.20 will show you some size data for copper tubing. Are you interested in size details for copper that is used for drain, waste, and vent (DWV) applications? Refer to Figure 11.21 for this information.
![]()
![]()

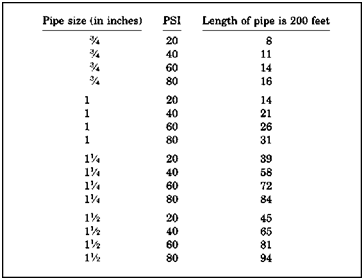 |
Copper is rated in terms of types. For example, Type K copper has a thick wall and is considered a stronger material than Type L or Type M copper. This type of tubing isn’t used often in residential work, but it is sometimes used for water services when the copper is supplied in its soft form. Soft copper comes in a roll and allows underground piping, such as that for a water service, to be installed without joints. Type L copper is frequently used for water distribution pipes in homes and can be used in its soft form for water services. A softer type of copper is known as Type M copper. This copper tubing is used mostly for hot-water-baseboard heating systems. it is available only in rigid lengths and is not available in a rolled coil. Many plumbing codes prohibit its use for water distribution systems. Figure 11.22 will show you how different types of copper are available for purchase.
|
Nominal pipe size (inches) |
Outside diameter (inches) |
Inside diameter (inches) |
|
Type К |
||
|
V* |
0.375 |
0.305 |
|
% |
0.500 |
0.402 |
|
Vi |
0.625 |
0.527 |
|
% |
0.750 |
0.652 |
|
% |
0.875 |
0.745 |
|
1 |
1.125 |
0.995 |
|
VA |
1.375 |
1.245 |
|
l’/i |
1.625 |
1.481 |
|
2 |
2.125 |
1.959 |
|
2Vi |
2.625 |
2.435 |
|
3 |
3.125 |
2.907 |
|
3Va |
3.625 |
3.385 |
|
4 |
4.125 |
3.857 |
|
5 |
5.125 |
4.805 |
|
6 |
6.125 |
5.741 |
|
8 |
8.125 |
7.583 |
|
10 |
10.125 |
9.449 |
|
12 |
12.125 |
11.315 |
|
Type L |
||
|
‘/4 |
0.375 |
0.315 |
|
% |
0.500 |
0.430 |
|
Vz |
0.625 |
0.545 |
|
% |
0.750 |
0.666 |
|
% |
0.875 |
0.785 |
|
1 |
1.125 |
1.025 |
|
VA |
1.375 |
1.265 |
|
v/i |
1.625 |
1.505 |
|
2 |
2.125 |
1.985 |
|
2 Vi |
2.625 |
2.465 |
|
3 |
3.125 |
2.945 |
|
3Vi |
3.625 |
3.425 |
|
4 |
4.125 |
3.905 |
|
5 |
5.125 |
4.875 |
|
6 |
6.125 |
5.845 |
|
8 |
8.125 |
7.725 |
|
10 |
10.125 |
9.625 |
|
12 |
12.125 |
11.565 |
FIGURE 11.20 ■ Copper tube – water distribution. [Courtesy of McGraw-Hill)

 |
Cast-iron pipe comes in three basic types.
One is known as service-weight pipe and another is called extra-heavy cast iron.
These types of pipe may be purchased with either one or two hubs. A third type of cast-iron pipe is called no-hub pipe.
This type has no hub on either end; it is coupled with mechanical joints (Fig.
11.24 & 11.25). Cast iron is still in use and provides years of dependable service.






Leave a reply