Multivariate normal distributions
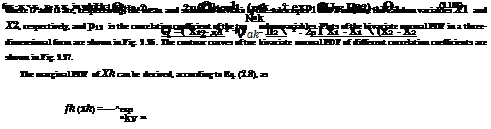 |
A bivariate normal distribution has a PDF defined as
for k = 1 and 2. As can be seen, the two random variables having a bivariate normal PDF are, individually, normal random variables. It should be pointed out that given two normal marginal PDFs, one can construct a bivariate PDF that is not in the form of a bivariate normal as defined by Eq. (2.108).
According to Eq. (2.17), the conditional normal PDF of X11 x2 can be obtained as
(2.109)
>■;
![]()
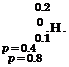 |
|||
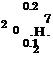 |
|||
.H.
0.1
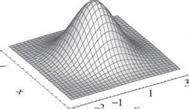
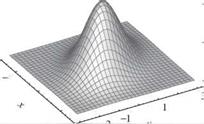
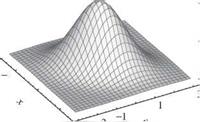
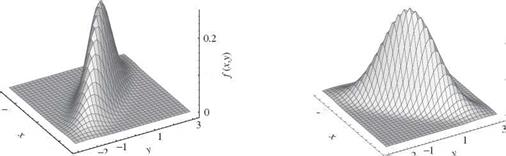
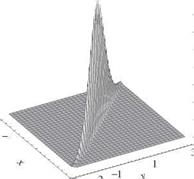
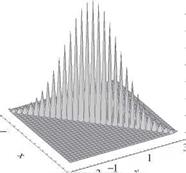 Figure 2.26 Three-dimensional plots of bivariate standard normal probability density functions. (After Johnson and Kotz, 1976.)
Figure 2.26 Three-dimensional plots of bivariate standard normal probability density functions. (After Johnson and Kotz, 1976.)

|
|
|
|
|
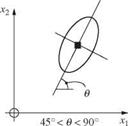
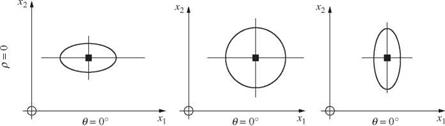
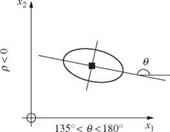
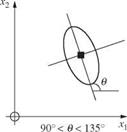

Figure 2.27 Contour of equal density of bivariate standard normal probability density functions. (After Johnson and Kotz, 1976.)
for —to < x1 < to. Based on Eq. (2.109), the conditional expectation and variance of the normal random variable X11 x2 can be obtained as
E(X1 | x2) = P1 + P12(ff1/V2)(x2 – P2) (2.110)
Var(X11 x2) = (1 – P22) (2.111)
Expressions of the conditional PDF, expectation, and variance for X2 | x1 can be obtained immediately by exchanging the subscripts in Eqs. (2.109) through (2.111).
![]()
For the general case involving K correlated normal random variables, the multivariate normal PDF is
in which і, = (д1, p.2,…, /гК )t, a К x 1 column vector of the mean values of the variables, with the superscript t indicating the transpose of a matrix or vector, and Cx is a К x К covariance matrix:
|
^11 |
012 |
■ ‘ ‘ p1K |
|
021 |
022 |
■ ■ ■ 02K |
|
Pk 1 |
pK 2 |
■ ■ ■ °KK_ |
|
Cov(X) = С, = |
This covariance matrix is symmetric, that is, Pjk = okj, for j = k, where ajk = Cov(Xj, Xk). In matrix notation, the covariance matrix for a vector of random variables can be expressed as
![]() С, = E [(X — і,)(X — і,)4
С, = E [(X — і,)(X — і,)4
In terms of standard normal random variables, Zk = (Xk — ik)’ak, the standardized multivariate normal PDF, can be expressed as
in which Rx = Cz = E (ZZ *) is a К x К correlation matrix:
|
1 |
P12 ■ |
■ P1K |
|
P21 |
1 ■ |
■ P2K |
|
PK1 |
PK2 ■ |
■ 1 |
|
Corr(X) = Cov(Z) = Rx = |
with pjk = Cov(Zj, Zk) being the correlation coefficient between each pair of normal random variables Xj and Xk. For bivariate standard normal variables,
![Multivariate normal distributions Подпись: (2m)!(2n)! minm,n) (2p^)2і 2m+n (m - І)!(n - І)! (2j)! (2m + 1)!(2n + 1)! (2p12)2 j 2m+n P12 (m - І )!(n - j )!(2j + 1)! E [Z2mZ2n+1 ] = 0 (2.115)](/img/1312/image272_1.png) |
|
the following relationships of cross-product moments are useful (Hutchinson and Lai, 1990):
for m and n being positive integer numbers.






Leave a reply