METAL ROOFING TYPES
![]()
![]()
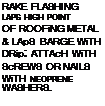 |
 |
metal ridge
![]()
![]()
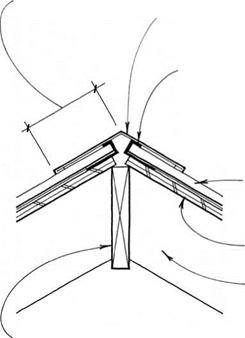
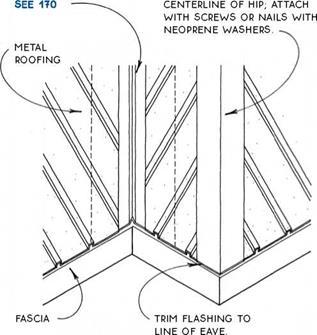 FLASHiNG MADE FRoM SAME MATERIAL AS
FLASHiNG MADE FRoM SAME MATERIAL AS
roofing
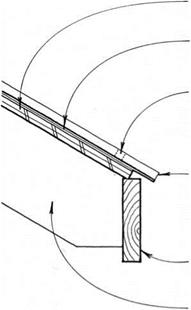
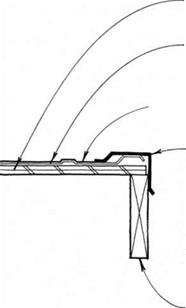
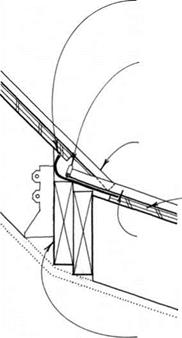
closure FLASHiNG at top of METAL roofing KEEPS out insects &
wiND-DRiVEN RAIN; FLASHiNG LAPS 30-LB. FELT uNDERLAYMENT.
![]()
 BEAD of caulking or SEALANT AT TOP EDGE oF
BEAD of caulking or SEALANT AT TOP EDGE oF
lower roofing panel forms a dam against wind-driven rain.
top roofing panel nests AGAINST lower PANEL, forming tight seal.
SHEATHING
pitch-change FRAMING SEE 133B
GUTTER HANGER TYPES SEE 195C
![]()
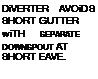
![]()
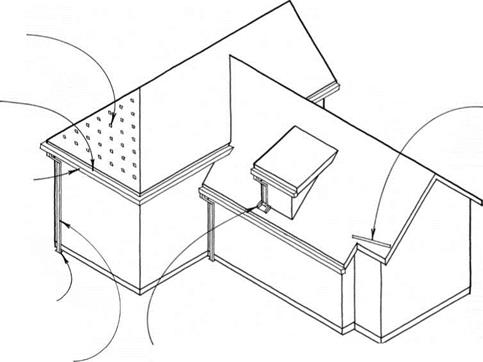 connect downspout TO DRAiN pipE or to splash block.
connect downspout TO DRAiN pipE or to splash block.
SEE 194
 |
 |
DOWNSpOUT FOR Every 40 FT. OF GUTTER






Leave a reply